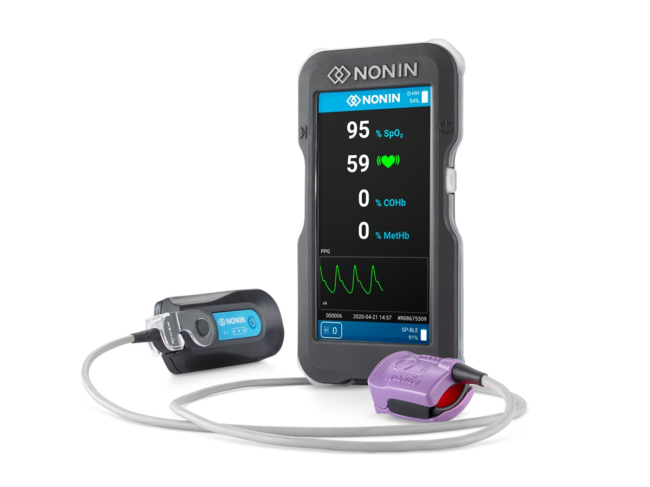
Plymouth, Minn.-based Nonin Medical Inc. gained a U.S. FDA 510(k) clearance for its Co-Pilot wireless hand-held multiparameter system (H500). The system is expected to be used by first responders to evaluate various oxygenation and respiratory-related parameters in patients after incidents such as cardiac arrest, traumatic injury, carbon monoxide or smoke inhalation.
It’s also expected to prove useful amidst the unfolding pandemic. Oxygen levels in the body are increasingly seen as helpful in establishing which patients will require hospitalization. Co-Pilot can simultaneously measure patient pulse oximetry (SpO2), pulse rate, carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) and methemoglobin (MetHb). With an additional sensor it can also measure cerebral and tissue oximetry (rSO2).
Assessing the damage
“With the COVID-19 pandemic, first responders around the globe have become a triage resource for hospitals not wanting to bring patients into a facility if not absolutely medically necessary. Co-Pilot’s wireless capabilities allow for patient and caregivers needs to be optimally met,” Nonin Vice President of Marketing Christine Horton told BioWorld.
“One of the unique clinical issues with COVID-19 is silent hypoxia – when blood oxygen saturation levels (SpO2) are low but there are few other warning signs,” she continued. “The ability to rapidly measure and respond may allow for faster diagnosis and treatment. With Co-Pilot, first responders can measure SpO2 and other patient health parameters from a distance to limit their exposure to the virus.”
Co-Pilot is the first handheld device to enable emergency responders to measure cerebral and tissue oximetry (rSO2), which had previously only been measurable in the hospital setting. After a cardiac arrest, this measurement is critical to determine the potential for a patient’s survival and brain function.
Roughly 330,000 cardiac arrest events occur outside of the hospital in the U.S. each year – and the prognosis is rarely good. Only 10.6% of these patients survive on average, while only 8.3% make it through with good neurological function.
“During our clinical study of the Co-Pilot (H500) we found it to be portable and extremely easy to use. The ability to track a multitude of parameters was beneficial and provided critical information for patient care,” said Guillaume Debaty, an emergency medicine physician at Grenoble Alpes University Hospital and the head of SAMU de l’Isère in Grenoble, France. “We also believe the technology has great potential for the management of cardiac arrest patients.”
COHb is a measure of carbon monoxide in the red blood cells after it has been inhaled, helping in the diagnosis and monitoring of carbon monoxide poisoning. MetHb is monitored typically to assess potential chemical exposure that results in hemoglobin that cannot bind to oxygen or carry it to tissues.
See Full Press Release at the Source: Nonin nabs FDA nod for wireless handheld for first responders to monitor oxygen indicators | 2020-07-08 | BioWorld
Written by: Stacy Lawrence
 Legacy MedSearch has more than 30 years of combined experience recruiting in the medical device industry. We pride ourselves on our professionalism and ability to communicate quickly and honestly with all parties in the hiring process. Our clients include both blue-chip companies and innovative startups within the MedTech space. Over the past 10 years, we have built one of the strongest networks of device professionals ranging from sales, marketing, research & , quality & regulatory, project management, field service, and clinical affairs.
Legacy MedSearch has more than 30 years of combined experience recruiting in the medical device industry. We pride ourselves on our professionalism and ability to communicate quickly and honestly with all parties in the hiring process. Our clients include both blue-chip companies and innovative startups within the MedTech space. Over the past 10 years, we have built one of the strongest networks of device professionals ranging from sales, marketing, research & , quality & regulatory, project management, field service, and clinical affairs.We offer a variety of different solutions for hiring managers depending on the scope and scale of each individual search. We craft a personalized solution for each client and position with a focus on attracting the best possible talent in the shortest possible time frame.
Are you hiring?
Contact us to discuss partnering with Legacy MedSearch on your position.